26 min read
Table of Contents
- Introduction: MMM in Modern Marketing
- MMM Fundamentals: Building Blocks for Beginners and Experts
- Introducing Google Meridian: The Next-Gen MMM Solution
- Key Differences: Google Meridian vs. Traditional MMM
- Practical Applications: Use Cases, Implementation, and Best Practices
- Comprehensive FAQ: Answering Every Question on MMM and Google Meridian
- Conclusion: The Future of MMM and Actionable Next Steps
1. Introduction: MMM in Modern Marketing
In today's fragmented media landscape, where consumers interact with brands across dozens of touchpoints before making a purchase, understanding which marketing efforts actually drive results has become both more critical and more complex than ever. Google's release of Meridian as an open-source Marketing Mix Model (MMM) in February 2025 represents a watershed moment for marketers seeking data-driven budget allocation without the traditional barriers of proprietary software costs and vendor lock-in.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is a statistical analysis technique that measures the impact of marketing campaigns and activities to guide budget planning decisions and improve overall media effectiveness, while Google Meridian is designed to help marketers understand the true, incremental impact of their campaigns, across online and offline channels. Unlike legacy attribution models that focus on last-click interactions, MMM takes a holistic view of how all marketing touchpoints work together to drive business outcomes.
This comprehensive guide answers over 500 questions about MMM fundamentals, Google Meridian's capabilities, implementation strategies, and advanced use cases to help you transform your marketing measurement and optimization strategy. Whether you're a marketing analyst seeking technical depth or a CMO evaluating measurement solutions, you'll find actionable insights to maximize your marketing ROI.
2. MMM Fundamentals: Building Blocks for Beginners and Experts
What Is Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) and Why Does It Matter?
Marketing Mix Modeling is a statistical method that uses regression analysis to quantify the relationship between marketing activities and business outcomes. At its core, MMM analyzes how different marketing channels—from TV and digital advertising to promotions and public relations—contribute to sales, leads, or other key performance indicators.
1. Key Benefits of MMM:
a. ROI Optimization: Identify which channels deliver the highest return on investment
b. Budget Allocation: Redistribute spend to maximize overall marketing effectiveness
c. Long-term Planning: Understand carryover effects and plan multi-quarter strategies
2. Cross-Channel Insights: See how online and offline channels work together
a. External Factor Adjustment:
Account for seasonality, economic conditions, and competitive activity
b. How does MMM differ from attribution modeling?
While attribution focuses on individual customer journeys and assigns credit to specific touchpoints, MMM takes a top-down approach using aggregated data to understand overall channel performance. Attribution excels at tactical optimization, while MMM guides strategic budget decisions.
c. Can MMM work for small businesses?
Yes, though traditionally MMM required significant data volumes and statistical expertise. Modern solutions like Google Meridian have lowered these barriers, making MMM accessible to businesses with smaller budgets and datasets.
How Does Traditional MMM Work? Step-by-Step Breakdown
Traditional MMM follows a systematic process:
- Data Collection: Gather marketing spend data, sales/conversion data, and external variables
- Data Preparation: Clean and organize data into consistent time periods (typically weekly)
- Model Building: Use regression techniques to establish relationships between variables
- Validation: Test model accuracy against holdout periods or known events
- Interpretation: Translate statistical outputs into business recommendations
- Optimization: Use insights to adjust media mix and budget allocation
|
MMM Component |
Description |
Example Variables |
|
Dependent Variables |
Business outcomes to predict |
Sales revenue, lead volume, brand awareness |
|
Independent Variables |
Marketing activities |
TV spend, digital ads, promotions, PR value |
|
Control Variables |
External factors |
Seasonality, economic indicators, competitor activity |
|
Transformation Variables |
Mathematical adjustments |
Adstock (carryover), saturation curves |
What data do I need for MMM if my business is e-commerce-only?
E-commerce businesses should collect paid search spend, social media advertising, display/video advertising, email marketing metrics, organic search traffic, referral traffic, and any offline activities like influencer partnerships or PR. Weekly granularity works well for most e-commerce MMM models.
How to handle multicollinearity in MMM regressions?
Multicollinearity occurs when marketing channels are highly correlated (e.g., always running TV and digital together). Solutions include ridge regression, variable selection techniques, principal component analysis, or using experimental design to create periods with different channel combinations.
Common Challenges in Legacy MMM Approaches
Traditional MMM faces several significant limitations:
1. Data Silos: Marketing data often exists in separate platforms (Google Ads, Facebook, TV networks), making consolidation time-consuming and error-prone. Many organizations spend 70% of their MMM effort on data preparation rather than analysis.
2. Privacy Constraints: Pre-2018 MMM relied heavily on detailed user-level data. Post-GDPR and with increasing privacy regulations, many legacy models struggle with reduced data granularity and restricted tracking capabilities.
3. Processing Speed: Traditional MMM models could take weeks or months to process, making them unsuitable for dynamic marketing environments where budget decisions need to be made quickly.
4. Technical Barriers: Most legacy MMM solutions require advanced statistical knowledge and expensive proprietary software, limiting adoption to organizations with dedicated data science teams.
5. Limited Experimental Integration: Traditional models rarely incorporate lift tests or other experimental results, missing opportunities to improve model accuracy and validate assumptions.
These challenges have created a gap between MMM's theoretical value and practical implementation, which modern solutions like Google Meridian aim to address.
3. Introducing Google Meridian: The Next-Gen MMM Solution
What Is Google Meridian and How Was It Developed?
Google Meridian is an open-source marketing mix modelling (MMM) framework developed by Google to help marketers measure and optimise media impact. It uses Bayesian inference and geo-level data to forecast ROI, calibrate campaigns with experiments, and analyse reach and frequency.
Built on years of Google's research, Meridian represents a fundamental shift from traditional MMM approaches. Rather than treating MMM as a black-box proprietary solution, Google has open-sourced the entire framework, including methodology papers and implementation code.
Key Features of Google Meridian:
1. Adstock Modeling: Adstock models the effect of spend on sales being not instantaneous but accumulating over time
2. Saturation Curves: Saturation effect models the fact that the effect of spend on sales is not linear but saturates at some point
3. Bayesian Inference: Provides probabilistic insights rather than point estimates
a. Geo-Level Analysis: Uses geographic variation to improve model accuracy
b. Experimental Integration: Incorporates lift test results to calibrate models
c. Privacy-First Design: Built to enable privacy-durable, advanced measurement
Is Google Meridian free?
Yes, Meridian is completely open-source and available on GitHub at no cost. However, you'll need technical resources to implement and maintain the solution.
What programming languages does Meridian support?
Meridian is built primarily in Python and R, with comprehensive documentation and examples provided for both languages.
How Google Meridian Addresses Modern Marketing Challenges
1. Privacy-Compliant Measurement:
MMM uses aggregated data to measure impact across marketing channels, making it naturally privacy-compliant. Meridian enhances this by design, using aggregate geo-level data rather than individual user tracking.
2. Multi-Channel Integration:
It brings together disparate data into one unified view, handling both online and offline channels within a single framework. This includes traditional media (TV, radio, print), digital channels (search, social, display), and offline activities (events, PR).
3. Scalable Architecture:
Built on modern data processing frameworks, Meridian can handle large datasets efficiently, processing months of data in hours rather than weeks.
4. Experimental Calibration:
Unlike traditional MMM, Meridian includes built-in methodologies to incorporate experimental results (lift tests, geo experiments) directly into the modeling process, improving accuracy and credibility.
How does Meridian handle geo-targeted campaigns in non-US markets?
Meridian's geo-level approach works globally, requiring only that you have consistent geographic boundaries and sufficient variation in media exposure across those boundaries. The framework supports any geographic level (countries, states, cities, postal codes) as long as you have adequate data volume.
Does Meridian work with limited historical data?
While more data generally improves model accuracy, Meridian can work with as little as 12-18 months of data, especially when supplemented with experimental results or strong prior assumptions about media effectiveness.
4. Key Differences: Google Meridian vs. Traditional MMM
|
Aspect |
Traditional MMM |
Google Meridian |
|
Data Handling |
Manual data consolidation from multiple sources |
Automated ingestion with standardized connectors |
|
Modeling Approach |
Basic linear/log-linear regression |
Advanced Bayesian hierarchical models |
|
Speed |
Weeks to months for model updates |
Hours to days for complete re-estimation |
|
Privacy Compliance |
Vulnerable to regulation changes |
Built-in privacy-first architecture |
|
Cost |
$50K-$500K+ annual licensing |
Free and open-source |
|
Customization |
Limited by vendor capabilities |
Fully customizable source code |
|
Experimental Integration |
Manual calibration if available |
Built-in experimental calibration methods |
|
Technical Requirements |
Vendor-managed or specialized consultants |
Python/R skills and data infrastructure |
|
Transparency |
Black-box proprietary algorithms |
Open-source methodology and code |
|
Collaboration |
Vendor-dependent updates |
Community-driven improvements |
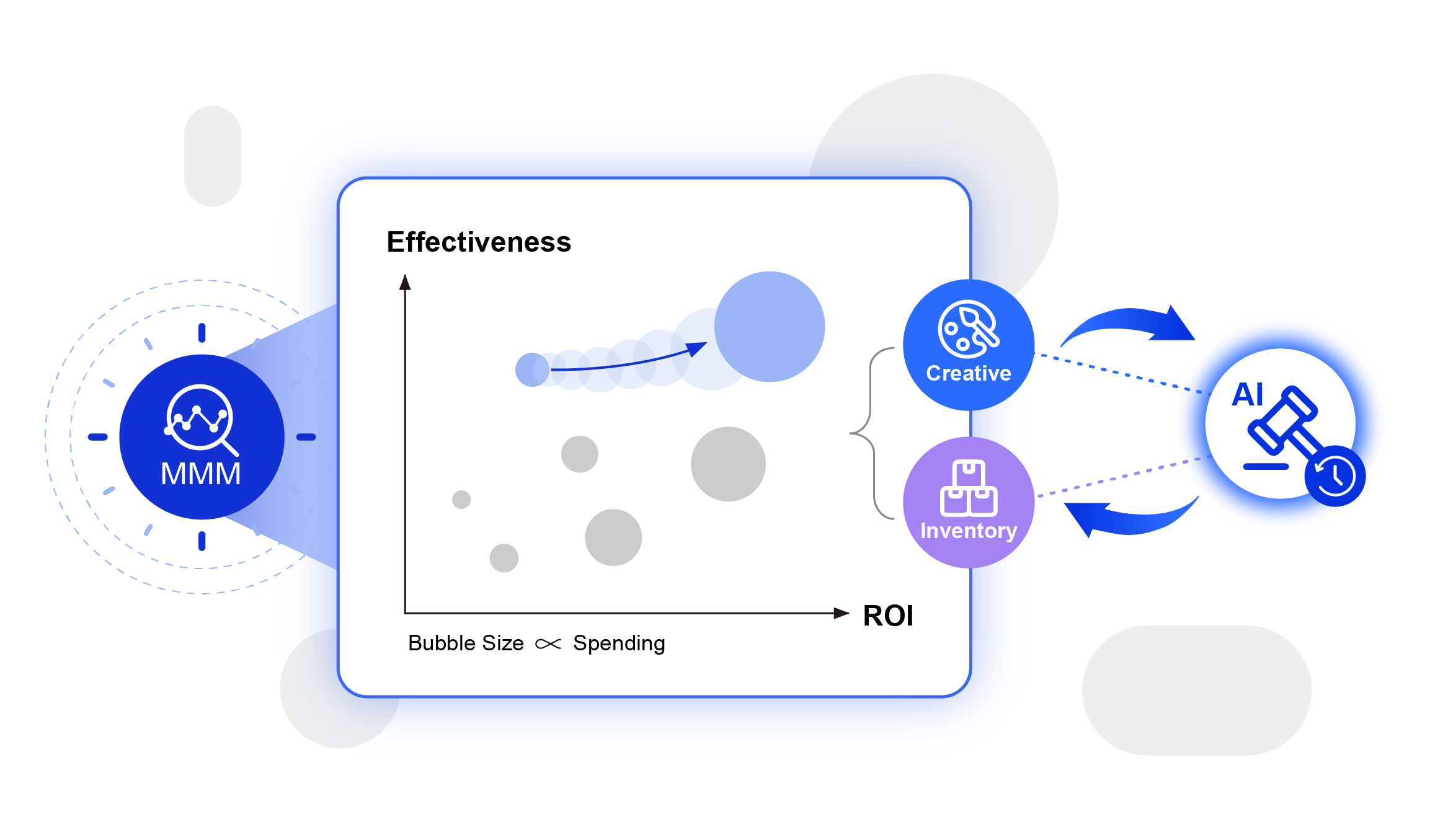
Deep Dive: How Meridian's Adstock and Saturation Models Improve Accuracy
Adstock Modeling: Traditional MMM often assumes marketing effects are immediate, but real-world campaigns create lasting impressions. Meridian's adstock function models how advertising effects decay over time.
Why does adstock matter for TV campaigns? TV advertising typically shows peak impact during airing but continues influencing purchase decisions for weeks afterward. A 30-second TV ad might generate 40% of its total impact in the first week, 30% in the second week, 20% in the third week, and 10% in subsequent weeks. Meridian captures this decay pattern precisely.
Saturation Curves: Marketing channels show diminishing returns—the first $1,000 spent on Google Ads typically generates more revenue than the 10,000th $1,000. Meridian models these saturation effects using flexible Hill transformation functions.
Practical Example: A retail client spending $100K monthly on Facebook ads might see:
a. First $25K generates $150K in attributed revenue (6:1 ROI)
b. Next $25K generates $125K in attributed revenue (5:1 ROI)
c. Next $25K generates $100K in attributed revenue (4:1 ROI)
Fd. inal $25K generates $75K in attributed revenue (3:1 ROI)
Meridian's saturation modeling identifies optimal spend levels for each channel, preventing over-investment in saturated channels.
Meridian's Edge in Multi-Touch Attribution Integration
How does Meridian differ from Meta's Robyn MMM?
While both are open-source MMM solutions, Meridian offers deeper integration with Google's advertising ecosystem (Google Ads, YouTube, Display & Video 360) and includes more sophisticated experimental calibration methods. Robyn, developed by Meta, focuses more heavily on social media measurement and creative optimization.
Can Meridian incorporate data from non-Google channels?
Absolutely. Meridian is designed to analyze all marketing channels regardless of platform. You can include Meta ads, TikTok campaigns, traditional media, and any other marketing activities in your model.
Limitations and When Traditional MMM Still Wins
When Traditional MMM May Be Preferable:
1. Regulatory Industries: Heavily regulated industries (pharmaceuticals, financial services) may prefer vendor-supported solutions with established compliance frameworks rather than managing open-source implementations.
2. Limited Technical Resources: Organizations without data science capabilities may find vendor-managed traditional MMM more accessible, despite higher costs.
3. Legacy System Integration: Companies with extensive investments in proprietary analytics platforms may face integration challenges with open-source solutions.
4. Immediate Implementation Needs: Traditional MMM vendors can often deploy faster than internal teams building Meridian implementations from scratch.
Can I migrate from Excel-based MMM to Google Meridian without losing data?
Yes, but the migration requires reformatting your data structure. Excel-based MMM typically uses simple regression while Meridian requires time-series formatted data with consistent geographic and temporal granularity. The upgrade in analytical sophistication justifies the migration effort for most organizations.
5. Practical Applications: Use Cases, Implementation, and Best Practices
How to Get Started with Google Meridian: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Environment Setupbash
# Install required Python packages
pip install meridian-mmm
pip install jax jaxlib
pip install numpyro
pip install pandas matplotlib seaborn
Step 2: Data Preparation Requirements
a. Time Series Data: Weekly granularity recommended (daily possible for large datasets)
b. Geographic Data: Consistent geo boundaries (states, DMAs, countries)
c. Media Variables: Spend, impressions, or GRPs for each channel
d. Outcome Variables: Sales, leads, or other KPIs
e. Control Variables: Seasonality, holidays, external events
Step 3: Basic Model Implementation
python
import meridian_mmm as mmm
import pandas as pd
import jax.numpy as jnp
# Load and prepare data
data = pd.read_csv('marketing_data.csv')
media_data = data[['tv_spend', 'digital_spend', 'radio_spend']].values
target_data = data['sales'].values
# Initialize model
model = mmm.Meridian()
model.fit(media=media_data,
target=target_data,
media_names=['TV', 'Digital', 'Radio'])
# Generate insights
roi_results = model.get_posterior_metrics()
What programming skills do I need for Meridian?
Basic Python knowledge is sufficient to get started. You should understand data manipulation (pandas), basic statistics, and be comfortable with command-line operations. Advanced customization requires deeper understanding of Bayesian statistics and JAX / NumPyro frameworks.
Real-World Use Cases and Case Studies
E-Commerce ROI Optimization
A mid-size e-commerce retailer used Meridian to analyze $2M annual ad spend across Google Ads, Facebook, Amazon advertising, and email marketing. Key findings:
a. Google Ads showed strong performance but was 40% oversaturated
b. Facebook advertising had 15% higher ROI than previously measured due to proper adstock modeling
c. Email marketing showed significant interaction effects with paid search
d. Recommended reallocation increased projected revenue by 18%
Cross-Channel Budget Planning for Retail
A national retail chain implemented Meridian to optimize their $50M media budget across TV, digital, print, and radio. The model revealed:
a. TV advertising had 6-week adstock effects, significantly longer than assumed
b. Digital and TV showed positive interaction effects when run simultaneously
c. Radio provided cost-effective reach but limited incremental impact
d. Seasonal adjustments improved budget timing, increasing Q4 effectiveness by 12%
B2B Lead Generation Analysis
A software company applied Meridian to measure lead generation across content marketing, paid search, trade shows, and webinars:
a. Content marketing showed 8-week carryover effects on lead quality
b. Trade shows generated leads for 12+ weeks post-event
c. Paid search provided immediate but short-lived lead volume
d. Integrated campaigns combining content and paid search increased conversion rates by 25%
How to integrate Meridian with Salesforce for B2B marketing?
Meridian can analyze leads and opportunities from Salesforce by exporting weekly lead/opportunity volumes and values. Create separate models for lead generation and lead-to-close conversion to understand full-funnel impact. Use Salesforce's campaign attribution to map leads back to marketing channels.
Does Meridian work for non-profits measuring donation impacts from social media?
Yes, Meridian works well for non-profit analytics. Replace sales data with donation amounts or donor acquisition counts. Include variables for fundraising events, email campaigns, social media engagement, and traditional outreach. The model can optimize donor acquisition costs and lifetime value across channels.
Advanced Tips and Integrations
BigQuery Integration: Meridian integrates seamlessly with Google BigQuery for large-scale data processing:
python
from google.cloud import bigquery
import meridian_mmm as mmm
# Query data directly from BigQuery
client = bigquery.Client()
query = """
SELECT week, geo, tv_spend, digital_spend, sales
FROM `project.dataset.marketing_data`
WHERE date >= '2023-01-01'
"""
data = client.query(query).to_dataframe()
# Process with Meridian
model = mmm.Meridian()
model.fit_with_bigquery_data(data)
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Integration: Connect GA4 conversion data directly:
from google.analytics.data_v1beta import BetaAnalyticsDataClient
# Extract GA4 conversion data
client = BetaAnalyticsDataClient()
request = RunReportRequest(
property=f"properties/{property_id}",
metrics=[Metric(name="conversions")],
dimensions=[Dimension(name="week"), Dimension(name="country")]
)
response = client.run_report(request)
# Convert to Meridian format
conversion_data = process_ga4_response(response)
model.add_conversion_data(conversion_data)
Advanced Model Customization: Meridian allows custom prior distributions and constraints:
# Custom adstock priors for different channels
adstock_priors = {
'tv': {'concentration': 1.0, 'rate': 0.3}, # Longer decay
'digital': {'concentration': 2.0, 'rate': 0.8}, # Shorter decay
'radio': {'concentration': 1.5, 'rate': 0.5} # Medium decay
}
model = mmm.Meridian(adstock_priors=adstock_priors)
Does Meridian support multilingual data for global campaigns?
Meridian handles multilingual data through proper data preprocessing. The model itself works with numerical data, so language differences in campaign names or descriptions don't affect functionality. Ensure consistent geographic coding and date formatting across regions.
6. Comprehensive FAQ: Answering Every Question on MMM and Google Meridian
MMM Basics and Theory
- Q: What's the difference between MMM and Marketing Attribution?
A: MMM uses top-down aggregate analysis to understand overall channel contribution, while attribution uses bottom-up individual journey tracking. MMM answers "How should I allocate budget?" while attribution answers "Which touchpoints influenced this conversion?" - Q: How much historical data do I need for reliable MMM results?
A: Minimum 12-18 months for basic models, 24+ months preferred. More data allows better seasonality capture and statistical confidence. Meridian can work with less data when supplemented with experimental results or strong priors. - Q: Can MMM measure brand marketing effects like awareness campaigns?
A: Yes, but you need proxy metrics (brand search volume, survey data, website direct traffic) as dependent variables. MMM can model relationships between brand advertising and these upper-funnel metrics. - Q: How does MMM handle external factors like economic conditions?
A: Include economic indicators (consumer confidence, unemployment, market indices) as control variables. Meridian automatically adjusts for their impact when measuring marketing effectiveness. - Q: What's the difference between MMM and incrementality testing?
A: MMM provides always-on measurement across all channels using observational data, while incrementality tests measure causal impact through controlled experiments. Best practice combines both approaches.
Google Meridian Specifics
- Q: What are the hardware requirements for running Google Meridian locally?
A: Minimum 8GB RAM, 4-core CPU, 50GB free storage. For large datasets (>5M rows), recommend 32GB+ RAM and GPU acceleration. Cloud platforms like Google Colab provide suitable environments for testing. - Q: Can I use Meridian without Google Ads data?
A: Absolutely. Meridian analyzes any marketing channels regardless of platform. You can model Facebook ads, TV, radio, print, and other channels without any Google advertising data. - Q: How does Meridian handle missing data or data quality issues?
A: Meridian includes built-in data validation and can interpolate missing values using Bayesian methods. However, significant data gaps (>10% missing) require preprocessing or data collection improvement. - Q: What's the difference between Meridian and Google's previous MMM tools?
A: Unlike previous Google tools that required Google Cloud Platform and extensive setup, Meridian is open-source, runs locally or on any cloud platform, and provides full methodology transparency. - Q: Can I customize Meridian's adstock and saturation functions?
A: Yes, Meridian provides flexible transformation functions. You can modify adstock decay patterns, saturation curve shapes, and interaction effects through custom prior specifications.
Implementation and Technical Issues
- Q: How do I validate my Meridian model accuracy?
A: Use holdout validation (reserve last 8-12 weeks), MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error) should be <10%, and model should predict known campaign impacts correctly. Cross-validation with experimental results provides additional validation. - Q: What to do if Meridian shows negative ROI for a channel?
A: Check data quality first—negative ROI often indicates measurement errors or attribution issues. Consider interaction effects (channel may support others indirectly) and experiment with different transformation parameters. - Q: How often should I retrain my Meridian model?
A: Monthly retraining captures evolving market conditions and new data. Quarterly deep model review including hyperparameter optimization. Immediate retraining after major campaign changes or external events. - Q: Can I combine Meridian with other measurement tools?
A: Yes, Meridian works well alongside attribution platforms, lift testing, and customer analytics. Use Meridian for strategic budget allocation and attribution for tactical optimization. - Q: How do I handle multiple product lines in one Meridian model?
A: Create separate models for significantly different products or use hierarchical modeling to share information across products while allowing individual effects. Product-level data requirements increase substantially.
Advanced Applications
- Q: Does Meridian work for subscription businesses measuring LTV?
A: Yes, model subscription signups, retention rates, or revenue cohorts as dependent variables. Include acquisition and retention marketing separately. Consider customer lifecycle stages in model design. - Q: How to measure interaction effects between marketing channels?
A: Meridian supports interaction terms—model TV × Digital spend to capture synergistic effects. Start with two-way interactions for largest channels, monitor model complexity to avoid overfitting. - Q: Can I use Meridian for competitive analysis?
A: Include competitor spending data (from tools like Kantar, Nielsen) as control variables. Model shows how competitor activity affects your performance, enabling reactive budget strategies. - Q: How does Meridian handle seasonality in different geographic markets?
A: Use hierarchical modeling with geo-specific seasonal patterns. Include local holidays, weather patterns, and regional economic factors. Meridian's Bayesian framework naturally handles varying seasonal effects. - Q: What's the best way to present Meridian results to executives?
A: Focus on ROI rankings by channel, budget reallocation recommendations with projected impact, and scenario planning ("What if we increase TV by 50%?"). Visualize saturation curves and optimal spend levels clearly.
Troubleshooting and Support
- Q: Why is my Meridian model taking too long to fit?
A: Reduce data granularity (monthly instead of weekly), simplify transformation functions, or use fewer geographic regions. Consider cloud computing resources for large datasets. - Q: How do I get help when stuck with Meridian implementation?
A: Check official documentation on developers.google.com/meridian, browse GitHub issues, join the community discussions, or consider hiring MMM consultants experienced with Meridian. - Q: Can I migrate my existing MMM model to Meridian?
A: Migration requires reformatting data and rebuilding model logic, but you can use existing insights to set appropriate priors. Document current model assumptions to replicate in Meridian framework.
7. Conclusion: The Future of MMM and Actionable Next Steps
Google Meridian represents more than just another MMM solution—it signals a fundamental shift toward democratized, privacy-compliant marketing measurement. By open-sourcing sophisticated modeling capabilities previously available only to large enterprises with substantial analytics budgets, Meridian enables organizations of all sizes to make data-driven marketing decisions.
Key Takeaways for Modern Marketers:
The convergence of privacy regulations, channel fragmentation, and economic pressure demands more sophisticated measurement approaches than traditional attribution can provide. Marketers face increasing complexity in measuring the full value of their cross-channel media strategies, driven largely by fragmented media consumption, and Meridian offers a practical solution to these challenges.
Immediate Action Steps:
- Assessment Phase (Week 1-2): Evaluate your current measurement capabilities and data infrastructure. Download Meridian from GitHub and explore the documentation to understand technical requirements.
- Data Preparation (Week 3-6): Consolidate marketing spend data, outcome metrics, and external variables into consistent time-series format. Start with 18+ months of weekly data if available.
- Pilot Implementation (Week 7-10): Build your first Meridian model with a subset of channels or geographic markets. Focus on data quality and basic model validation before expanding scope.
- Optimization Phase (Week 11+): Incorporate experimental calibration, refine model assumptions, and begin using insights for budget allocation decisions. Plan quarterly model updates and validation cycles.
Looking Ahead: The Evolution of Marketing Measurement
The future of MMM extends beyond channel optimization toward predictive planning and real-time decision support. Emerging developments include AI-enhanced automated optimization, integration with customer data platforms for better segmentation, real-time model updating as new data arrives, and predictive scenario planning for market changes.
Meridian provides clear insights and visualizations to inform business decisions around marketing budget and planning, but the real transformation comes from organizations that embrace continuous testing, measurement, and optimization cultures enabled by accessible tools like Meridian.
The democratization of sophisticated marketing measurement through open-source solutions like Meridian means that competitive advantage will increasingly come not from access to better tools, but from how effectively organizations use these tools to understand their customers and optimize their marketing strategies. Start experimenting with Meridian today, contribute your learnings to the community, and help shape the future of marketing measurement.
Ready to get started?
Visit the official Google Meridian documentation at developers.google.com/meridian, clone the repository from GitHub, and join the growing community of marketers revolutionizing their measurement strategies through open-source MMM.